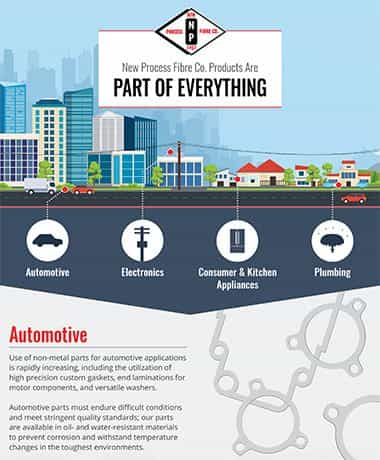
New Process Fibre Inc. Products are a PART OF EVERYTHING
Learn More![]()
“We are very busy making oxygen manifold systems for tent hospitals. We couldn’t do this important work without the quality parts that NPF
provides to Flotec!”
![]()
“Purchased plastic worked well for our application. We got good results with our vacuum-forming project”
![]()
“Always great dealing with your company. Thank you for your great service!”
![]()
“All in all, very easy to work with, very responsive. Received product as discussed in timely fashion with fast feedback!”
![]()
“Customer service have been wonderful to work with! They respond to any questions fast and help with any problems!”
Check Out Our NEW Video!
Our family business has always been committed to improving products, maximizing quality, and maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Watch Our VideoHave a Question? Ask Our Experts.
Get In TouchNeed help sooner? Dial 800.497.4520 for immediate assistance.
Stamping Services
Fabrication services
New Process Fibre has been Stamping and Die Cutting Non-Metallic Washers, Spacers, Gaskets, Shims and many other Custom Shapes for a variety of customers since 1927.